The Cardiovascular System
Handy hint!
This system moves blood around the body. It is often also referred to as the circulatory system.
Cardiovascular System diagramThe Cardiovascular System
The main function of the cardiovascular system is to move blood around our body as a fuel supply. This movement of blood helps to:
- Transport oxygen and nutrients to vital organs and muscles in the body.
- Transport carbon dioxide (and other waste products) away from vital organs and muscles.
- Transport hormones to cells in the body.
- Regulate body temperature.
- Protect the body against disease and infection.
- Stop bleeding after injury by clotting.
The cardiovascular system comprises the heart, blood and blood vessels. Click on the buttons below to learn more.
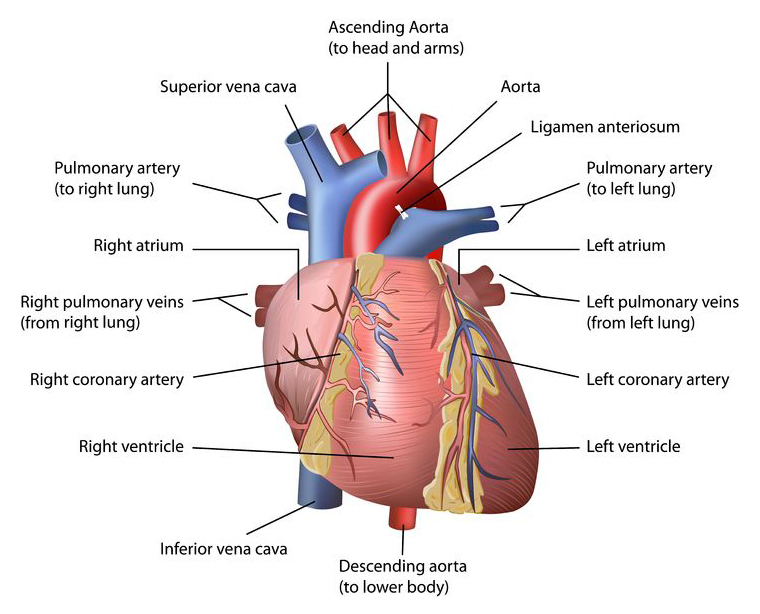
The heart
The heart is a muscle which is continually contracting and relaxing, in order to pump blood through the blood vessels. Every time the heart contracts and relaxes is called a ‘heartbeat’.
The heart is made up of four chambers. The top two are called the atria (left and right) and the bottom two are called the ventricles (left and right). The heart also has valves, which stop the blood from flowing backwards.
Blood vessels
Blood vessels allow the blood to flow throughout the body. There are three major types and these are:
- Arteries – These blood vessels have thick walls and carry oxygenated blood away from the heart through the aorta. They do not have valves.
- Veins – These blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood toward the heart. They have thinner walls than arteries, and they also have valves to make sure that the blood does not flow backwards.
- Capillaries – These are the smallest blood vessels in the body. They transport blood from the arteries to the veins and are very thin to allow oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide and other waste products to pass through their walls.