The Skeletal System
Handy hint!
This system supports and protects the body, while giving it shape and movement.
Skeletal System diagramThe Skeletal System
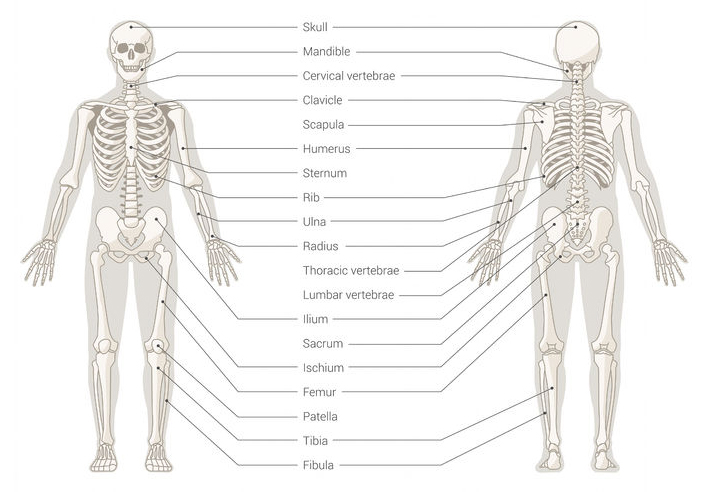
The skeletal system is made up of bones that join together to form joints. The skeletal system allows movement to happen when it is joined up with the muscular system. Connective tissue links the bones to the muscles.
The main functions of the skeletal system are:
- Working with muscles to allow movement in joints
- Giving support to our muscles and organs
- Protecting vital organs (for example, our skull protects our brain)
- Maintaining our basic body shape
- Producing red and white blood cells (this is done in the bone marrow)
- Storing minerals, such as calcium.
Now click on the buttons below to learn more about bones, joints and tissue.
Bones
The skeletal system is made up of 206 bones. These bones can be separated into four different types:
- Long bones, such as the femur (your thigh bone). These bones are usually connected with large movements of the body.
- Short bones, such as the carpals and tarsals (found in your hands and feet). These bones are linked to smaller movements of the body.
- Flat (or plate) bones. These bones protect the internal organs – for example, the skull and the ribs.
- Irregular bones. These bones are irregular in shape, such as the vertebrae (in your spine).
Joints
Joints come in three types – they can either be free moveable (extremely flexible) joints, immovable joints (where the bones are fused together and don’t move, such as in your skull) or moveable joints (which have restricted movement, like your toes). All movement occurs at joints (simply any point where two bones meet).
Your moveable joints can be separated into the following categories:
- Hinge joint – such as the ankle, elbow and knee.
- Ball and socket joint – such as the hip and shoulder.
- Pivot joint – such as the neck.
- Saddle joint – such as the thumb.
- Gliding joint – such as the bones in the palm of the hand.
- Condyloid joint – such as the wrist.
Connective tissue
Movement of the body is able to take place when the bones of the skeleton are connected to the muscles. Connective tissue links these bones and muscles.
There are three types of connective tissue:
- Tendon – this is a very strong, non-elastic band of tissue that connects muscle to bone.
- Cartilage – this is firm but flexible tissue that cushions bones at joints.
- Ligament – this is a short band of tough, flexible fibres connecting bones or cartilage. Ligaments also help to hold joints together.