Measuring devices
Assessment
In your Assessment at the end of this Unit, you will be asked to:
- Describe how measuring devices are used in engineering drawing.
This will help you to satisfy assessment criterion 1.2 for this Unit. It will also contribute to criterion 2.3, where you’ll need to demonstrate that you can use these devices! You’ll find lots of useful information on the following pages to help you complete this part of your assessment.
Let’s start by taking a look at some of the pieces of drawing equipment that are commonly used – you probably have some of these in your school! Click through the slider below to see a picture and description of each item.
-
Drawing board
This is used to place the drawing paper on when you are going to draw by hand. It can either stand up or be placed on a desk.
-
Pencil
There’s more to a good drawing pencil than just keeping it sharp! There are different levels of hardness, thickness, and softness. A HB pencil is great for general drawing. The higher the number on the pencil, the softer it is.
-
Retractable or Mechanical pencil
A mechanical pencil is used in the same way as a normal pencil, except that it contains interchangeable leads in different sizes and grades! These different leads make it a great tool for lots of different purposes, including drawing centre lines, dimensioning and lettering.
-
Engineers steel rule
These are steel rulers that come in a range of sizes, usually between 3 and 15cm in length. They can be accurate to 0.5mm if used carefully! Steel rulers are used to measure the straight lines of an engineering item before it is transferred to the drawing. Measurement units start right at the end of the ruler so there are no gaps to take into account.
-
Pair of compasses
You will use a compass when you need to draw circles or arcs. They are adjustable and can often be locked into position. Some compasses will have a holder for a standard pencil, while others have replaceable lead! Whichever type you use make sure the lead is sharp!
-
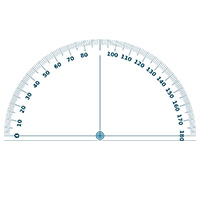
Protractor
A protractor is used to measure and produce angles on a drawing. They come in two sizes – a half protractor like the one in this picture, and a full protractor which looks like a full circle. A half protractor has a scale of up to 180 degrees, while a full protractor can measure up to 360 degrees. Both types of protractor are usually made from see-through plastic, and are accurate to 1 degree.
-
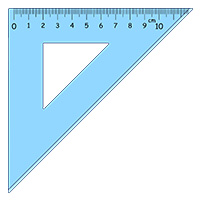
Set square
A set square is used to set the correct angle in a drawing. The sides are usually set at 30 and 60 degrees, while the corner is at 90 degrees, so that you can draw a perfect right angle! Some setsquares are adjustable, which means that you can change the angles to any degree for your drawing.
-
Dividers
Dividers are used to work out the distance between two points accurately, by placing one point in each place, and measuring the distance between them. This distance can then be transferred on to an engineering drawing. Dividers can be useful, but are only as accurate as the person using them!
-
Tape measure
A tape measure is used to measure larger objects, including length, width and depth. They are usually available in lengths of 2 – 25 metres. Tape measures can usually measure to an accuracy of 1mm.
-
Micrometre
A micrometre is used to measure the diameter or thickness of a component. They are available in different sizes from 0 – 25mm to around 150mm. To use them, simply place the item you want to measure in the gap, and turn the thimble until the spindle just reaches the object, and use the ratchet stop to adjust the spindle to the correct pressure before taking measurements. A standard micrometre is accurate to 0.01mm.
-
Venire calibre
A venire calibre is also used to measure the diameter or thickness of a physical engineering object, and they also have a depth measurement! They are easier to use than a micrometre because the measurement is displayed in a digital format, but you must make sure to zero the reading before you use them. Like micrometres, they are accurate to 0.01mm.
-
French curves
French curves are used when drawing by hand to achieve accurate curves. They are usually made from plastic and don’t offer any units of measurement, but are still more accurate than trying to draw curves by hand!
As you can see, there are lots of different measuring devices that can be used in engineering drawings! Some are used to take measurements, whilst others are used to convert these measurements into a drawing. Even though you may not use all of these tools when producing a drawing, it is important that you know what they are for, so that you can use this knowledge in your Assessment.
Think first
Can you think of a practical example of when you might use each piece of drawing equipment? Discuss your ideas with a friend before you move on.
Now let’s move on to Page 6 to learn about scale.